THERMODYNAMICS LAWS
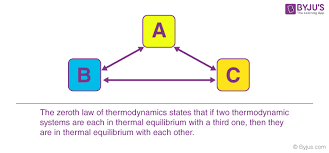
Laws of thermodynamics Zeroth Law 👽 The zeroth law of thermodynamics states: If two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. This statement implies that thermal equilibrium is an equivalence relation on the set of thermodynamic systems under consideration. Systems are said to be in equilibrium if the small, random exchanges between them (e.g. Brownian motion ) do not lead to a net change in energy. This law is tacitly assumed in every measurement of temperature. Thus, if one seeks to decide whether two bodies are at the same temperature , it is not necessary to bring them into contact and measure any changes of their observable properties in time. The law provides an empirical definition of temperature, and justification for the construction of practical thermometers. The zeroth law was not initially recognized as a separate law of thermodynamics, as its ...


